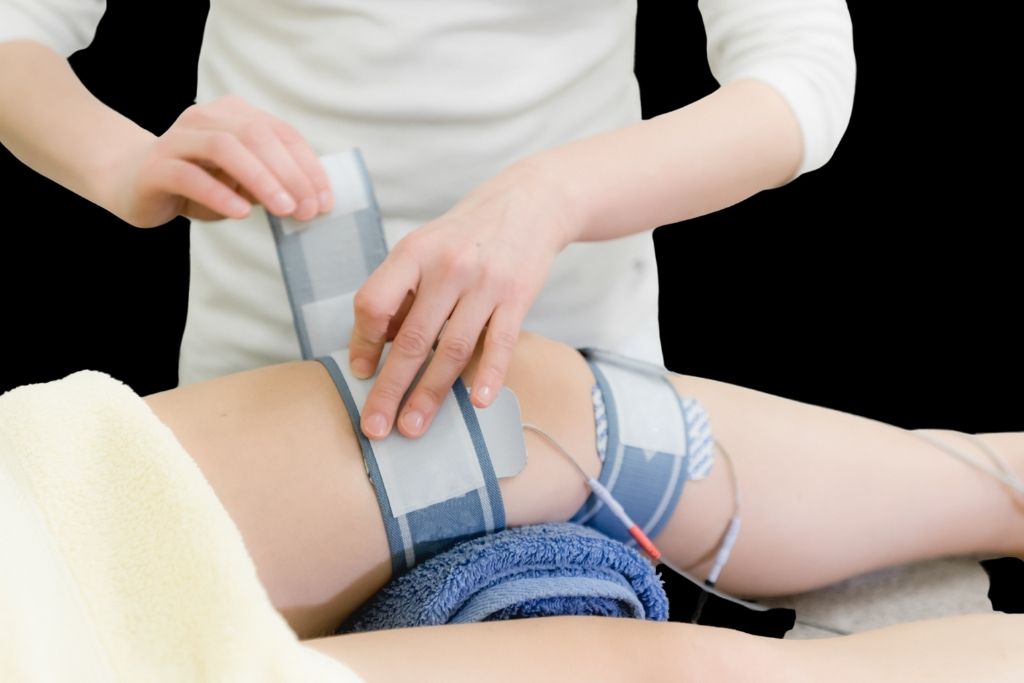
In today’s fitness and rehabilitation world, Electrical Muscle Stimulation (EMS) is gaining widespread popularity for its numerous health benefits, particularly in the realm of injury recovery. From top-tier athletes to physical therapy patients, EMS is revolutionizing the way we approach recovery and muscular healing. Whether you’re dealing with chronic pain, recovering from surgery, or looking to accelerate post-workout recovery, EMS could be a game-changing addition to your routine.
In this blog, we’ll explore what EMS is, how it works, and more importantly, how Electric Muscle Stimulation Training for Injury Recovery can support your healing journey.
What is Electrical Muscle Stimulation (EMS)?
Electrical Muscle Stimulation, or EMS, involves using low-level electrical impulses to stimulate muscles externally. These impulses mimic the signals sent by the central nervous system, causing your muscles to contract and relax. This technology has been used for decades in physical therapy, but with advances in modern devices, Electrical Muscle Stimulation is now accessible for fitness and wellness use.
The concept might sound futuristic, but it’s based on the same principle your body naturally uses to move, only enhanced and targeted for maximum therapeutic benefit.
The Science Behind EMS
EMS devices use electrodes attached to the skin, delivering controlled electrical pulses to specific muscle groups. When applied correctly, EMS can:
- Increase blood flow
- Improve muscle strength
- Decrease muscle soreness
- Speed up muscle recovery
- Reduce inflammation
- Aid in the regeneration of muscle tissue
By artificially stimulating the muscles, EMS mimics exercise in a controlled, low-impact environment. This is especially beneficial for individuals recovering from injuries, where conventional exercises may not be feasible or safe.
EMS and Injury Recovery: A Perfect Match
Injuries can limit mobility, reduce muscle strength, and impair blood flow. Traditional physical therapy can be slow, especially when patients are restricted from weight-bearing or high-impact exercises.
This is where EMS Training for Injury Recovery comes into play. EMS allows patients to stimulate muscles without physical strain. As a result, it helps prevent muscle atrophy and promotes circulation, even when traditional exercises are off-limits.
1. Prevents Muscle Atrophy
One of the biggest challenges during injury recovery is muscle atrophy due to inactivity. When muscles aren’t used, they begin to weaken. Electric Muscle Stimulation Training for muscle building helps prevent this by maintaining muscle activity without causing further damage or stress to the injury site. By simulating natural contractions, EMS can keep muscles engaged and strong, even when the patient is on bed rest or restricted from movement.
2. Improves Blood Circulation
Injury often leads to swelling and reduced blood flow, which can delay recovery. EMS enhances circulation by increasing muscle contractions, helping to flush out toxins and deliver nutrients to the damaged tissues. Improved blood flow reduces swelling and inflammation, which translates to quicker healing and less discomfort.
3. Reduces Pain and Inflammation
EMS is widely used for pain management. The gentle electrical pulses stimulate nerve fibers, blocking pain signals from reaching the brain. It also releases endorphins—your body’s natural painkillers—offering immediate relief. So whether you’re dealing with a sprained ankle, torn ligament, or post-surgical discomfort, EMS Training for Injury can play a pivotal role in reducing pain without the need for heavy medication.
4. Enhances Muscle Re-Education
After an injury, especially one involving nerves or prolonged immobility, muscles can “forget” how to function properly. EMS helps in re-educating muscles by stimulating correct movement patterns. This is especially important in neurological recovery scenarios such as stroke rehabilitation or spinal injuries, where muscle coordination is compromised. With targeted EMS protocols, patients can regain muscle function more efficiently.
5. Speeds Up Recovery Time
The ultimate goal of any recovery protocol is to get you back on your feet as quickly and safely as possible. EMS Training for Injury Recovery accelerates this process by addressing multiple facets of healing simultaneously: pain management, muscle maintenance, circulation, and neuromuscular retraining. With regular EMS sessions integrated into your rehab plan, you’re likely to experience faster results compared to traditional therapy alone.
Applications of EMS in Different Injuries
Electric Muscle Stimulation Training for Injury is versatile and can be tailored for various injury types:
1. Sports Injuries: From ACL tears to hamstring pulls, EMS in sports can be very helpful as it helps maintain muscle tone and support healing while athletes are sidelined.
2. Post-Surgical Recovery: After surgery, patients often deal with limited mobility. EMS helps in maintaining muscle function and reducing stiffness without physical exertion.
3. Orthopedic Injuries: In cases like fractures or dislocations, EMS is used to maintain muscle integrity and improve the healing environment.
4. Neurological Conditions: Conditions like stroke, multiple sclerosis, or spinal cord injuries benefit from EMS by promoting neuro-muscular communication.
The Role of EMS in Physical Therapy
Many physical therapists integrate EMS into their sessions, particularly in the early stages of recovery. It is a valuable supplement to manual therapy and traditional exercises. EMS helps reduce the reliance on pharmaceutical pain management, which can come with long-term side effects.
Furthermore, as patients progress, EMS can be used in conjunction with functional movements to enhance outcomes, rebuild strength, and improve confidence in the injured area.
EMS for Athletes: Beyond Recovery
Athletes not only use EMS for injury recovery but also as a proactive tool. Professional teams incorporate EMS into their regular training to reduce muscle fatigue, enhance recovery, and improve performance. For example, after intense workouts or games, EMS helps flush out lactic acid and rejuvenate muscle tissue, reducing soreness and downtime.
Is EMS Safe?
When used under professional supervision or as directed by certified EMS personnel, electrical stimulation is safe and well-tolerated. It’s non-invasive, drug-free, and customizable for individual needs. However, EMS is not recommended for people with pacemakers, epilepsy, or certain skin conditions unless cleared by a medical professional. Always consult with your doctor or physiotherapist before starting EMS therapy.
Final Thoughts
Injury recovery can be a slow and frustrating process. But with modern tools like Electrical Muscle Stimulation, the journey becomes more efficient, comfortable, and results-driven. Whether you’re a professional athlete or a weekend warrior, Electric Muscle Stimulation Training for Injury offers a scientifically backed, low-impact method to support your recovery and get you back to doing what you love—faster and safer. By investing in EMS Training, you’re not just speeding up your healing—you’re ensuring that your recovery is effective, long-lasting, and empowering.