In today’s fast-paced world, finding effective, time-saving ways to stay fit has become more important than ever. That’s where EMS training—short for electrical muscle stimulation training—comes in. Whether you’re an athlete looking to boost performance, someone recovering from injury, or simply aiming to get in shape, EMS offers a powerful and innovative alternative to traditional workouts. By sending electrical impulses to stimulate your muscles directly, EMS can help build strength, improve endurance, and tone your body in a fraction of the time.
You may have come across EMS training and wondered if it’s really worth the attention. The truth is, electrical muscle stimulation (EMS) is more than just a passing trend—it’s a scientifically supported method that’s revolutionizing fitness training. Whether you’re aiming to build muscle, enhance recovery, or make the most of your workout time, EMS can deliver impressive results. Let’s take a closer look at how it works, what’s happening inside your body, and why so many people are embracing this innovative fitness approach.
What Is EMS Training?
EMS training, or electro-muscle stimulation training, is a fitness technique that uses low-frequency electrical impulses to trigger muscle contractions. These impulses mimic the brain’s natural signals, causing the muscles to contract even without voluntary movement. It allows you to activate more muscle fibers in less time, using wearable suits, patches, or belts with embedded electrodes. Whether for fitness, rehabilitation, or performance, EMS offers a unique way to improve strength, tone, and endurance safely and efficiently.
How Electrical Muscle Stimulation Works
EMS training uses controlled electric impulses to mimic brain signals and stimulate muscle activity. These impulses are delivered through electrodes placed on the skin, helping muscles contract and relax rhythmically. Here’s a step-by-step breakdown of how EMS works during a training session.
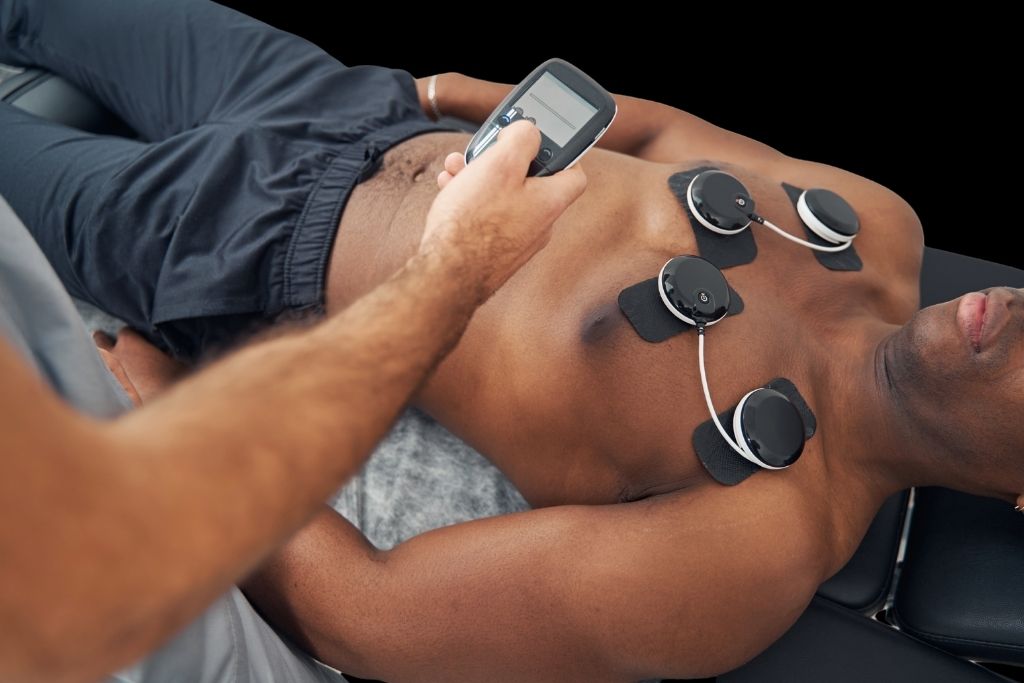
1. Electrode Placement
Electrodes are placed directly on your skin over specific muscle groups like the abs, arms, glutes, or thighs. These electrodes are usually part of a specialized EMS suit or belt. Proper placement is essential for targeting the right muscles and ensuring optimal stimulation. A certified EMS trainer ensures that each electrode aligns perfectly with the muscles you want to activate, improving both efficiency and safety.
2. Signal Transmission
Once the electrodes are in place, the EMS muscle trainer sends low-frequency electrical impulses to them. These impulses travel through the skin and into the muscle tissue, mimicking the action potentials your nervous system naturally produces. The strength and frequency of these impulses can be adjusted based on your comfort and training goals. This step ensures deep muscle engagement and replicates the effect of traditional strength training.
3. Nerve Activation
The electrical impulses bypass the brain and central nervous system, going straight to the motor neurons. This direct stimulation causes muscle fibers to contract without requiring voluntary movement. By activating these nerves directly, EMS is especially effective in recruiting muscles that are often neglected or difficult to engage with regular training, particularly deeper stabilizing muscles.
4. Muscle Contraction
The motor neurons respond to the impulses by triggering muscle contractions, just as they would during conventional exercise. These contractions feel intense and controlled, simulating the same effort as lifting weights. Once the impulse stops, the muscle relaxes. This cycle of contraction and relaxation mimics the mechanics of real workouts, providing a full-body stimulus without excessive strain on joints or tendons.
5. Repeated Cycles
Throughout a session, your muscles repeatedly contract and relax in cycles guided by the EMS device. These cycles can be synchronized with simple body movements or even static holds. Over time, these controlled repetitions help build strength, improve endurance, and increase muscle tone. The rhythmic nature of EMS training helps reduce fatigue while maximizing muscle engagement in just 20 to 30 minutes per session.
What’s Happening Inside Your Body?
Beyond what you feel on the surface, EMS triggers several internal processes that contribute to its effectiveness. From activating fast-twitch fibers to improving blood flow and neuromuscular function, here’s what’s really happening inside your body during EMS.
1. Fast-Twitch Muscle Activation: EMS targets hard-to-reach fast-twitch muscle fibers responsible for strength and explosive movement. These fibers are often underutilized in standard workouts but are critical for performance. By activating them directly, EMS enhances power, muscle mass, and athletic output more efficiently than conventional exercise alone.
2. Enhanced Blood Flow: The rhythmic contractions caused by EMS improve circulation to the stimulated muscles. Increased blood flow helps deliver oxygen and nutrients, flushes out toxins, and promotes quicker recovery. This benefit is especially valuable for injury rehab and post-exercise recovery, making EMS a therapeutic tool as well as a fitness method.
3. Improved Neuromuscular Connections: Repeated EMS sessions strengthen the connection between your brain and muscles. This improved communication enhances motor control, balance, and muscle coordination. Over time, it leads to better posture, more fluid movement, and increased control during physical activities, even those outside the gym or EMS studio.
Benefits of EMS Fitness Training
EMS isn’t just a gimmick—it’s backed by science and used worldwide for various health, fitness, and performance goals. Here are some of the key benefits of EMS training:
1. Efficient Muscle Building: EMS can target up to 90% of muscle fibers in a session, compared to around 60% in conventional training. This makes EMS training for muscle building an excellent tool for hypertrophy.
2. Time-Saving Workouts: A 20-minute EMS session can provide the same muscular stimulus as a 90-minute gym workout. It’s perfect for busy professionals or those who prefer short, intense training.
3. Low Impact on Joints: Because EMS doesn’t require heavy weights or complex movements, it’s joint-friendly—ideal for people with mobility issues or recovering from injuries.
4. Rehabilitation and Recovery: EMS is widely used in physiotherapy to rebuild muscle strength, prevent atrophy, and rehabilitate injured areas. If you’ve searched for “EMS trainer” in a medical setting, this is the type of training they use.
5. Posture and Core Stability: EMS training stimulates stabilizing muscles, improving posture and balance. It’s particularly effective in strengthening the core.
6. Fat Loss and Toning: The increase in muscle activity leads to higher caloric burn, helping with fat reduction and body toning. Many EMS studios offer programs tailored for slimming and toning goals.
What to Expect in an EMS Session
Trying EMS training near me for the first time? Don’t worry—the process is smooth and guided by professionals. Here’s a breakdown of what typically happens during a session so you know exactly what to expect.
- Initial Consultation: Your first EMS session starts with a one-on-one consultation. The trainer will ask about your fitness goals, medical history, and current activity level. This helps them tailor your EMS program to suit your needs—whether it’s for fat loss, muscle building, or recovery.
- Suit Up: You’ll be given a special EMS suit or have pads placed on your skin over target areas. The suit is designed with built-in electrodes that connect to the EMS device. It’s comfortable, flexible, and easy to wear, allowing full-body stimulation without restricting your movement.
- Warm-Up: A light warm-up, such as walking or gentle stretching, prepares your body and muscles for stimulation. This phase helps increase circulation and enhances the effectiveness of the EMS impulses by activating your muscles before the real contractions begin.
- Training Begins: As the session starts, your trainer gradually increases the intensity of the impulses. You’ll perform basic movements or remain stationary as the device cycles through contractions. The intensity is personalized, so you’ll feel a firm contraction without discomfort, similar to a deep tissue massage.
- Cool Down and Recovery: The session ends with a cool down, where the EMS device sends gentler impulses or the trainer guides you through stretches. This helps relax the muscles, prevent soreness, and improve recovery. Some studios also offer post-session massages or hydration to further enhance the benefits.
Final Thoughts
EMS training is changing the game in fitness, offering a smart, time-efficient, and science-based way to get stronger, leaner, and healthier. Whether you’re a busy professional, athlete, senior, or rehab patient, EMS adapts to your goals and lifestyle. With minimal joint impact and maximum muscle activation, it provides real results in just 20 minutes a session.
So if you’re interested in trying out EMS training or working with a professional EMS trainer, now is the perfect time to explore this innovative fitness approach. With consistent training and proper guidance, EMS can help you build muscle, tone your body, and feel great—all while saving time. Experience the power of electric muscle stimulation for muscle building and see how it can transform your fitness journey.